Syphilis Antibodies – Qline
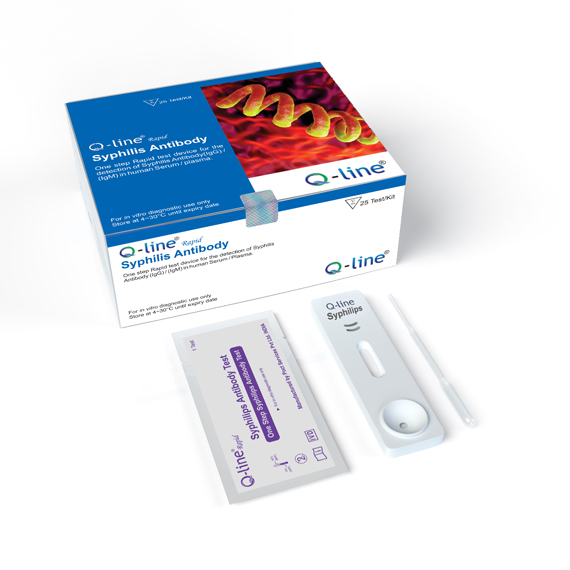
Q-Line Rapid Syphilis Antibodies
Product Features:-
- Built for superior performance that offers reliable results
- No need of highly trained staff and expensive equipment.
- Simple to perform.
- Easy interpretation of results
- Rapid result in 20 minutes.
- Storage at room temperature (4~30° C).
Description
Syphilis is an infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum that is most often spread by sexual contact, such as through direct contact with a syphilis sore (chancre), a firm, raised, painless sore. The most common syphilis tests detect antibodies in the blood that are produced in response to a T. pallidum infection. Syphilis is easily treated with antibiotics but can cause severe health problems if left untreated. An infected mother can also pass the disease to her unborn child, with serious and potentially fatal consequences for the baby. There are several possible stages with syphilis:
Primary syphilis—the primary stage begins about 2-3 weeks after being infected. During the first (primary) stage of syphilis, patient may notice a single sore or multiple sores. The sore usually lasts 3 to 6 weeks and heals regardless of whether or not you receive treatment.
Secondary syphilis—if primary syphilis is left untreated, secondary syphilis may occur from 6 weeks to 6 months after the chancre first appears. This stage usually starts with a rash on one or more areas of body. Other symptoms patients may have can include fever, swollen lymph glands, sore throat, patchy hair loss, headaches, weight loss, muscle aches, and fatigue
Late, tertiary syphilis—if untreated, secondary syphilis may continue into a latent stage, during which an infected person has no symptoms but continues to have the infection, and this stage can last for years. In these cases, the bacteria can damage the heart, eyes, brain, nervous system, bones, joints, or almost any other part of the body.
Q-Line® Rapid Syphilis Antibody Test (device) is an immunoassay for the rapid and visual detection of antibodies to Treponema pallidum in human serum or plasma to aid in the diagnosis of syphilis.